How Does The Brain Learn New Things
Abstract
The by few years accept been marked by a large number of discoveries almost the learning brain. Those insights take the potential to support teachers in designing even ameliorate classroom environments to help y'all acquire meliorate. While understanding the brain tin can exist helpful for teachers, this knowledge can as well exist beneficial for y'all as a pupil. For instance, it tin can encourage you to believe in your capacity to amend your own skills. Such beliefs brand it more than likely for y'all to make an endeavor and to make better apply of supportive learning strategies [1]. In this article, nosotros briefly present some core principles of the learning brain and suggest learning strategies inspired by neuroscience for you to try at schoolhouse or at home.
What Happens in My Brain When I Am Learning?
Your brain is primarily composed of well-nigh 85 billion neurons, which is more than than the number of stars you can see with the naked eye in the night heaven. A neuron is a cell which acts as a messenger, sending data in the form of nervus impulses (like electrical signals) to other neurons (come across Figure 1). For example, when you are writing, some neurons in your brain ship the "move fingers" bulletin to other neurons and this message then travels through the nerves (similar cables) all the mode to your fingers. The electrical signals that are communicated from i neuron to another are therefore what allows you lot to exercise everything you lot do: write, retrieve, see, spring, talk, compute, and so on. Each neuron can exist connected with up to 10,000 other neurons, leading to a large number of connections in your encephalon [2], which looks like a very dense web (see Figure two).
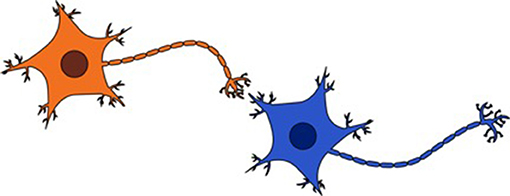
- Figure 1 - Figure illustrating 2 neurons that are connected.
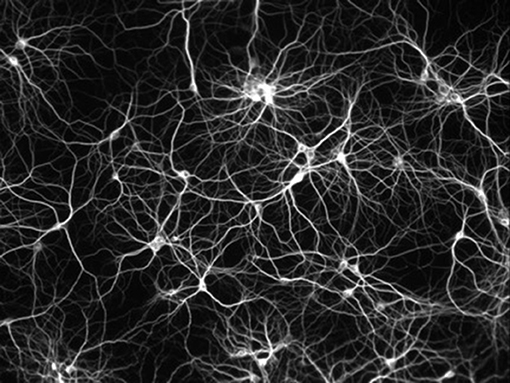
- Figure two - Effigy illustrating the very big number of connections between neurons.
When yous are learning, important changes have place in your brain, including the creation of new connections between your neurons. This phenomenon is chosen neuroplasticity . The more you lot practice, the stronger these connections become. As your connections strengthen, the messages (nerve impulses) are transmitted increasingly faster, making them more efficient [3]. That is how you lot become ameliorate at annihilation you larn whether it is playing football, reading, cartoon, etc. We can compare the connections betwixt your neurons to trails in a forest (see Figure iii). Walking through a wood without a trail is difficult, because you have to compact and push button the vegetation and branches out of the way to carve your fashion through. Only the more than you use the aforementioned trail, the easier and more practicable it becomes. Conversely, when y'all terminate using the trail, the vegetation grows back, and the trail slowly disappears. This is very similar to what happens in your brain—when you stop practicing something, the connections between your neurons weaken and tin can ultimately be dismantled or pruned. That is why it may seem so hard to beginning reading once more when school starts if you lot have not read all summertime. However, it is possible for some neural networks to get so strong that the trails or connections never completely disappear.
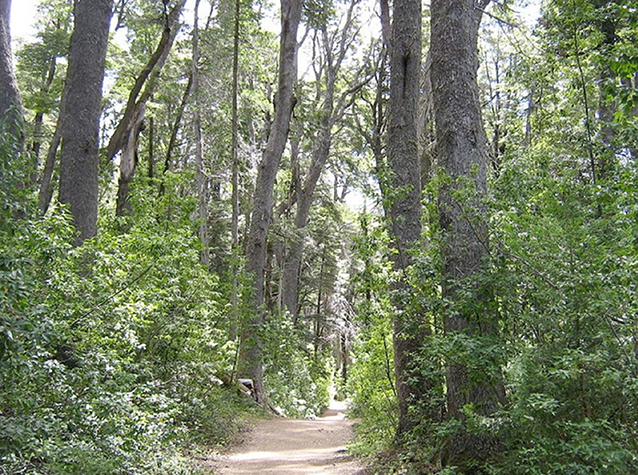

- Figure 3 - Figure illustrating the analogy of the trail in the wood.
The fact that learning rewires your neurons shows how dynamic (plastic) your brain is—that the brain changes and does not remain fixed. Practicing or rehearsing repeatedly activates your neurons and makes y'all learn. These changes happen as early as when a baby is in their female parent's womb and continues throughout a person'south life. So, the question is, how tin you help your neurons to create and strengthen their connections? Here, we present two strategies that appear to be more uniform with how your encephalon works and could help you learn better.
Which Learning Strategies Are More than Uniform With Your Brain?
Strategy 1: Repeatedly Activating Your Neurons
Because the connections between your neurons need to be activated multiple times to become stronger and more efficient, a start and crucial strategy is to repeatedly activate them. This ways that to learn arithmetic tables for instance, you have to practice it repeatedly, to establish the "trail" between your neurons. As a baby, y'all were not able to speak and walk within 1 day: y'all expert a lot. Notwithstanding, it is important to notation that but reading or glancing at your arithmetics tables will not be that helpful in connecting your neurons. You might as well observe it quite disengaging and slow. To create the connections between your neurons, you need to retrieve the arithmetic tables from your memory. In other words, you accept to try recall the answer yourself to activate your connections. We are not saying that this is easy to do! However, scientists remember that this "struggle" improves learning because the claiming is an indication that y'all are building new connections. Recollect, learning something new is like hiking in a bush with no designated trail, you will probably walk slowly at first, merely if you keep hiking, trails will start forming and eventually you will be walking on well-beaten tracks. Too, when you exercise try to call up what you accept learned and make a mistake, it tin can help you identify gaps in your learning and give y'all an indication of which trail notwithstanding needs to exist worked on.
Scientists have likewise noted that performing tests or exams tin help yous remember data better than studying alone [4]. For case, if yous report your arithmetic tables interspersed with test periods, you will probably perform better on your final exam than if you had merely studied. Why? The tests require that you retrieve the information from the neurons in which the data is stored, thus activating your connections and contributing to their strengthening. The point is thus to practice retrieval in an engaging way. At that place are different strategies that y'all could try at home, for example answering practice questions or using flashcards. These should improve learning more than re-reading or listening to lectures (as long as y'all do not flip the flashcard over before recalling the answer!). Other strategies include preparing questions to ask to a classmate or a parent as well as redoing tests or exercises. Apply your imagination! What you demand to remember is that first, for your neurons to strengthen their connections, you need to retrieve the information and avoid just reading or listening to the respond. 2d, you lot should program a way to get feedback to know whether you got something correct or wrong. Practise non be discouraged if yous face challenges, this is a natural step of the learning process taking identify in your encephalon!
Strategy two: Spacing the Activation of Neurons
Now that you know that neurons demand to be activated repeatedly for learning to occur (and that information technology ways retrieving information), you probably wonder how often you should practice. Scientists who study the learning brain observed that breaks and sleep betwixt learning periods heighten learning and minimize forgetting [5]. It therefore seems meliorate to retrieve often within spaced practice sessions, as opposed to a massed practice (practicing a task continuously without rest). For instance, instead of studying or doing homework for three h, afterward which yous would probably feel exhausted anyway, you could dissever this learning menstruum into three one-h periods or fifty-fifty into six half-an-hour periods. In short, when spacing your retrieval do, you let your brain to brand the connections that y'all strengthened during your do sessions more efficient. When y'all accept a quick break from practicing, allow us say a 20 min recess, yous allow for the maintenance or replacement of the receptors on the surface of the neurons. The receptors are like electric outlets that receive the nervus impulse (electrical signals) from other neurons. Taking a interruption helps them work better: your neurons tin can thus transmit their nerve impulses more hands to other neurons. Finally, when yous go a night of sleep between practise sessions, you lot actually benefit from a free retrieval practice session because while you slumber, your brain reactivates the connections between the neurons that you activated during the mean solar day. You could too go similar benefits from a nap. Adjacent time you find yourself sleepy in class, you could tell your instructor that you are in fact trying to do retrieval practice! In brief, when spacing out learning, and especially retrieval exercise, your brain is more than activated than when you lot mass learn in one long session.
At this bespeak, you are probably request yourself how to space out learning in your day-to-day life. The practiced news is that at that place are a number of ways to exercise it and it tin be easily adapted to dissimilar skills, such as solving mathematical issues or memorizing definitions. The most obvious change you can make to your study schedule is to interruption up sessions into smaller sessions. You could as well enquire your teacher to set daily or weekly review quizzes and other assignments. Finally, spacing can be done past doing interleaved do. This consists of a gear up of problems arranged so that consecutive problems cannot be solved past the same strategy. For case, you could mix your math problems so that geometry questions, algebra, or inequality problems are randomly sequenced. The added benefit of interleaving is that you appoint in unlike activities in-between two sessions, making good use of your time. In brief, ane thing to keep in mind is that data that was previously learned will crave less attempt to re-learn because the spacing gives your brain time to consolidate—meaning your brain produces the building blocks required for the connections between your neurons.
Conclusion
Your brain is where learning occurs and you lot therefore need to keep your neurons agile to optimize the utilise of class or study time. The two learning strategies proposed in this article have the potential to assistance you learn better past creating optimal weather condition to strengthen and consolidate the connections between your neurons. You now know that yous tin get better by repeatedly using the "trails" in your encephalon and past spacing out your practice. This greater understanding of how your brain learns and the use of supportive learning strategies can now permit you to help your brain learn improve!
Glossary
Neuroplasticity: ↑ The ability of your brain to modify, that is to create, strenghten, weaken or dismantle connections between your neurons.
Repeatedly Activating Your Neurons: ↑ Practicing a lot, trying to recall information from your memory, for example by explaining a concept to a friend or answering quiz questions.
Spacing the Activation of Neurons: ↑ Practicing more often merely for a shorter period. For example, instead of studying for 2 h in a row, studying 4 periods of 30 min over a few days allows your encephalon to have breaks and sleep which helps you think improve in the long run.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or fiscal relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We would like to wholeheartedly give thanks those who assisted in the translation of the manufactures in this Collection to make them more attainable to kids exterior English-speaking countries, and for the Jacobs Foundation for providing the funds necessary to interpret the articles. For this article, we would especially similar to give thanks Nienke van Atteveldt and Sabine Peters for the Dutch translation.
References
[1] ↑ Blanchette Sarrasin, J., Nenciovici, 50., Brault Foisy, L.-G., Allaire-Duquette, 1000., Riopel, 1000., and Masson, South. 2018. Furnishings of inducing a growth mindset in students past teaching the concept of neuroplasticity on motivation, achievement, and brain activity: a meta-analysis. Trends Neurosci. Educ. 12:22–31. doi: 10.1016/j.tine.2018.07.003
[ii] ↑ Rossi, S., Lanoë, C., Poirel, North., Pineau, A., Houdé, O., and Lubin, A. 2015. When i met my brain: participating in a neuroimaging report influences children's naive heed-brain conceptions. Trends Neurosci. Educ. 4:92–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tine.2015.07.001
[3] ↑ Kania, B. F., Wronska, D., and Zieba, D. 2017. Introduction to neural plasticity mechanism. J. Behav. Brain Sci. vii:41–eight. doi: 10.4236/jbbs.2017.72005
[4] ↑ Zaromb, F. Yard., and Roediger, H. L. 2010. The testing issue in free recall is associated with enhanced organizational processes. Mem. Cogn. 38:995–1008. doi: 10.3758/MC.38.8.995
[5] ↑ Callan, D. E., and Schweighofer, Northward. 2010. Neural correlates of the spacing effect in explicit verbal semantic encoding support the scarce-processing theory. Hum. Brain Mapp. 31:645–59. doi: ten.1002/hbm.20894
How Does The Brain Learn New Things,
Source: https://kids.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frym.2020.00054
Posted by: taylorwhick1956.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Does The Brain Learn New Things"
Post a Comment